Student Project done by:
XIE Fangjing (54102636)
The slides can be downloaded hereDownload
Background
In humans, myocardial infarction (MI) causes irreversible cell loss and scarring and is a major source of morbidity and mortality.
Statistics show that each year about 870,000 new cases are diagnosed in the United States and about 50 percent of those diagnosed will die within five years (Mozaffarian et al. 2015).
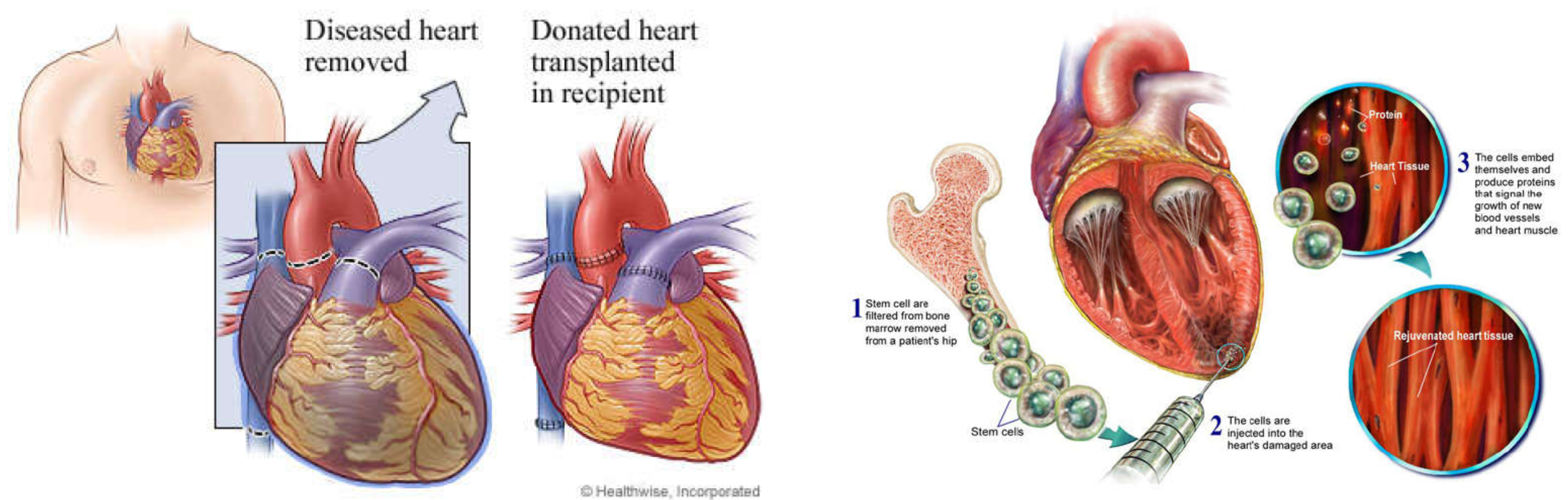
Heart transplant is restricted for the short of donated hearts.
There still many technical and biological obstacles that restrict successful application of stem and progenitor cells approachs. Cardiac stem and progenitor cells are extremely rare populations and their qualities are declined with age.
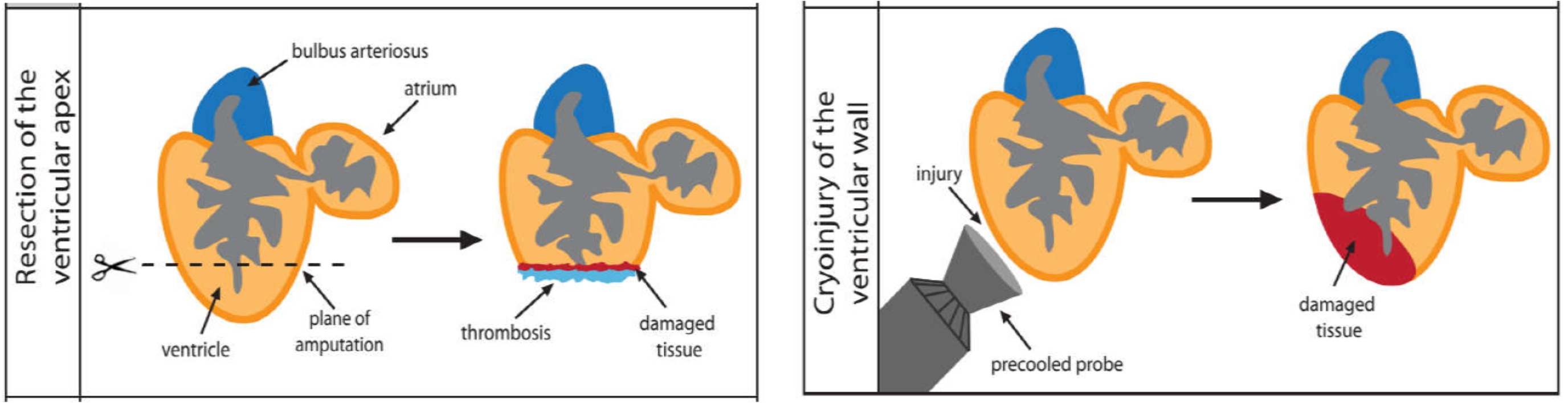
On the other hand, the adult zebrafish possess a highly efficient capacity in heart regeneration after ventricular resection or cryoinjury. Zebrafish have been a powerful low vertebrate model for studying heart regeneration.
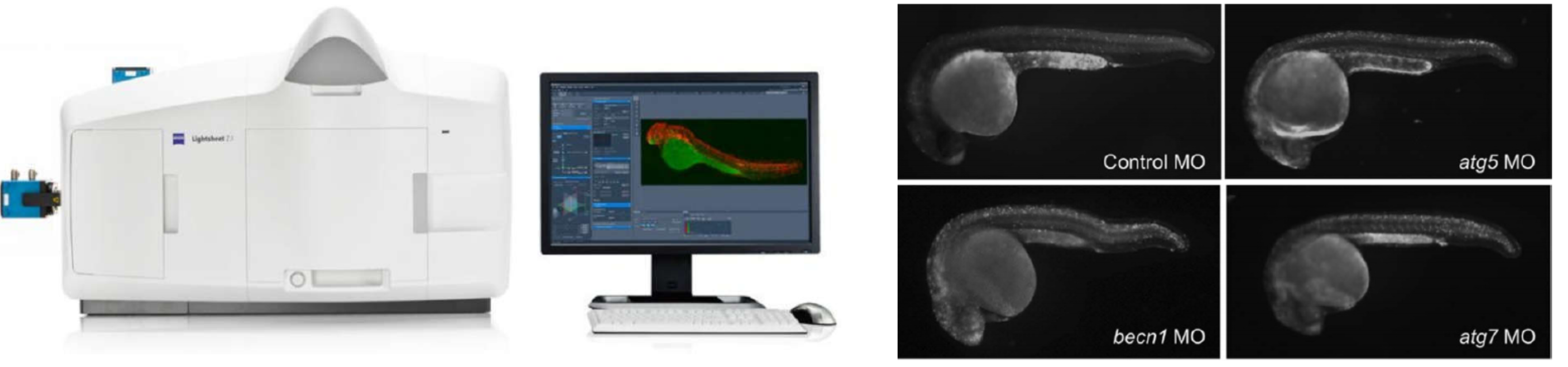
RNA-seq Data Analysis
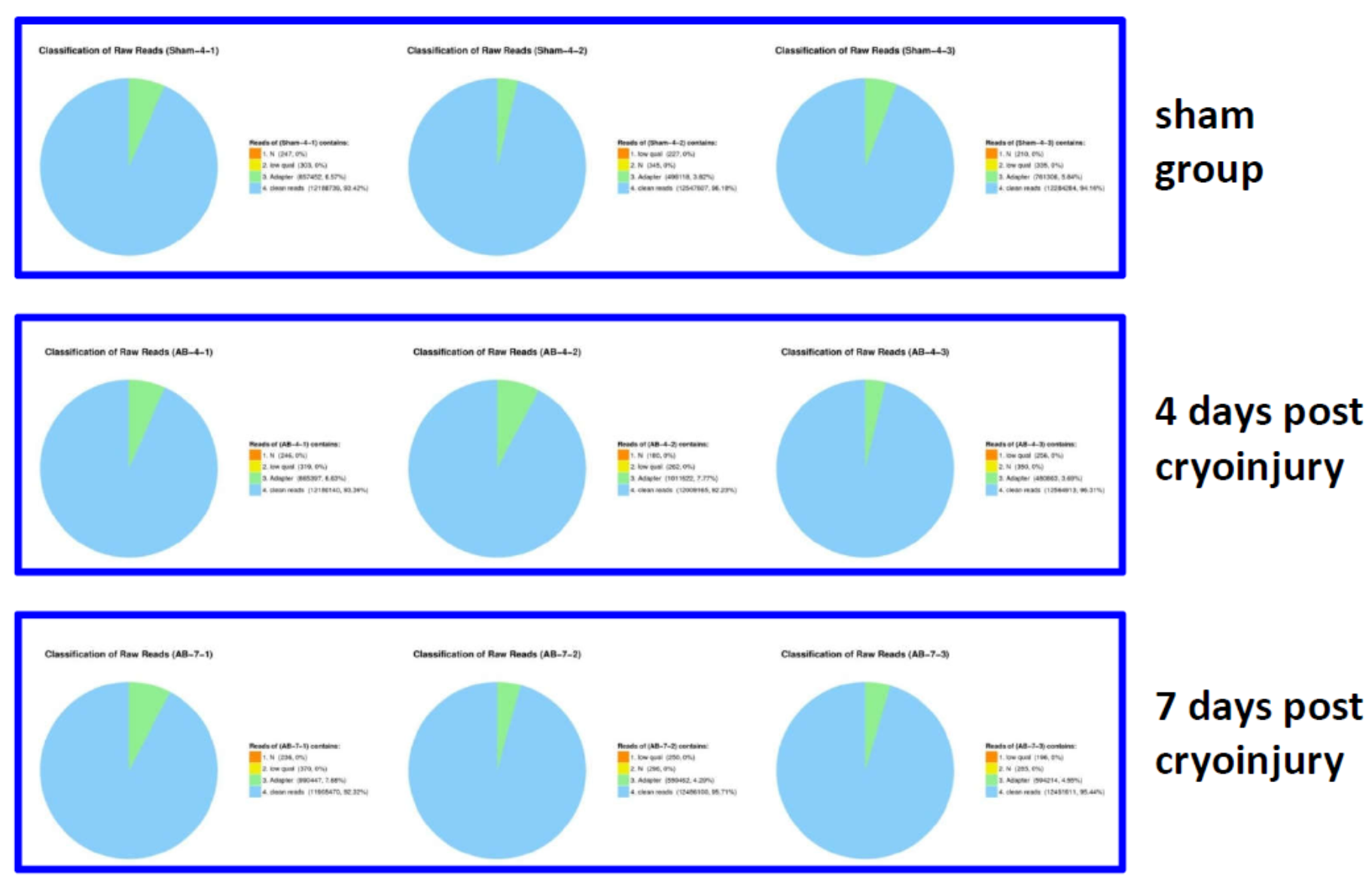
Classification of raw reads. Total of 9 samples were sequenced, average raw reads number is 13,026,869; besides the adapter and low quality reads, average 12,290,892 (94.35%) clean reads were generated.
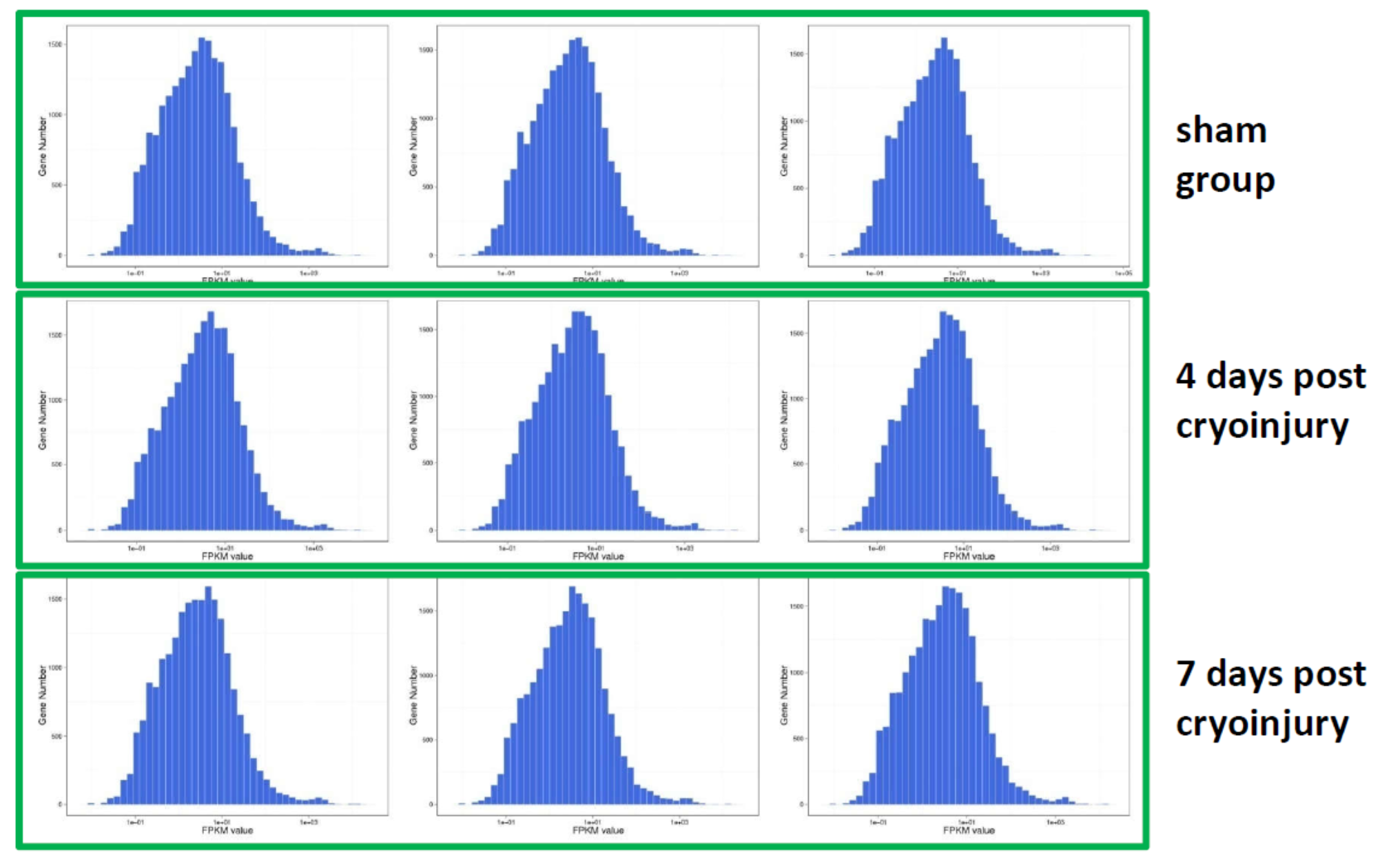
FPKM values mainly distribute from 1e-01 to 1e+03, and RNA-seq data fit a Negative Binomial distribution.
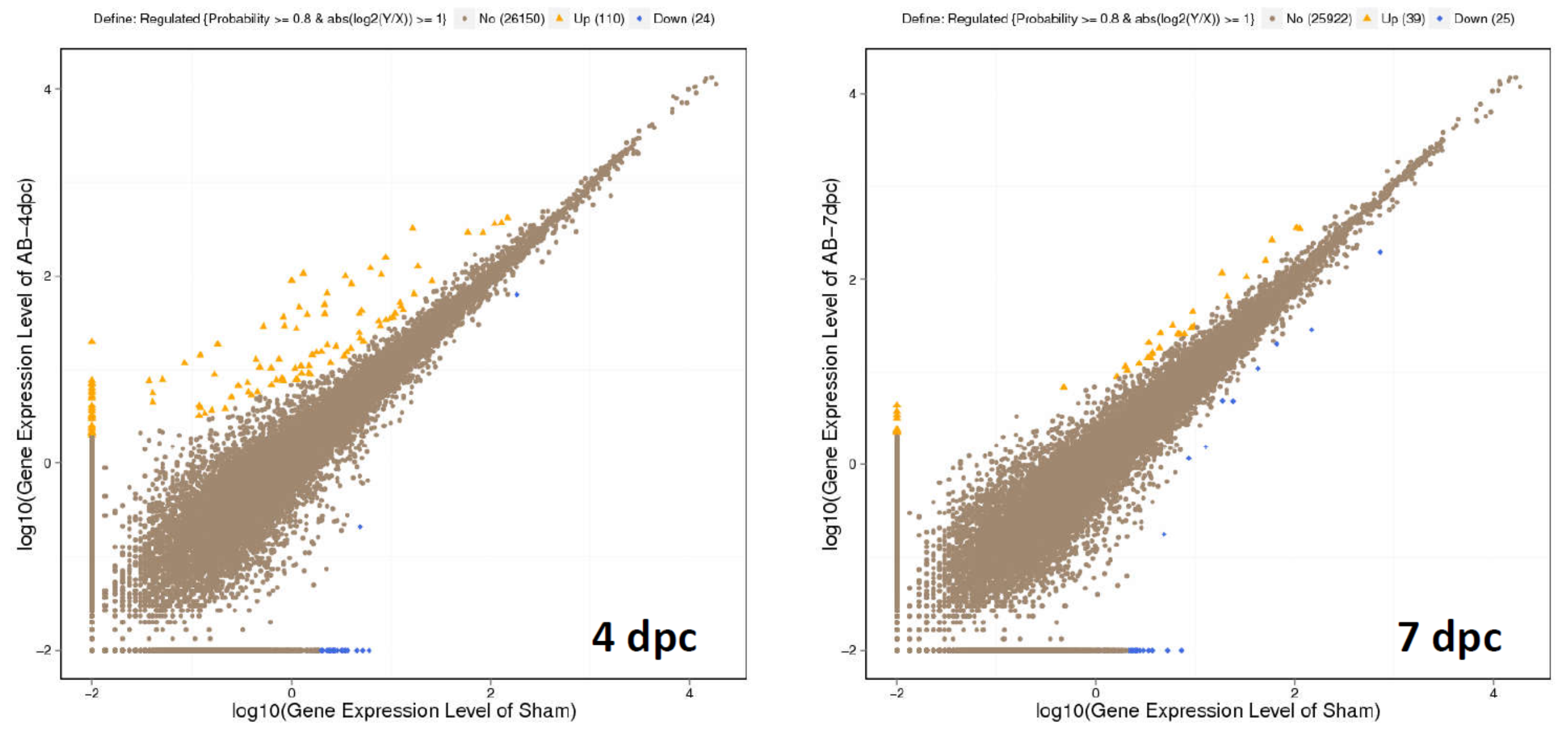
Differential genes expression showed 110 up-regulated genes and 24 downregulated genes at 4dpc, and 39 up-regulated genes and 25 down-regulated genes at 7dpc.
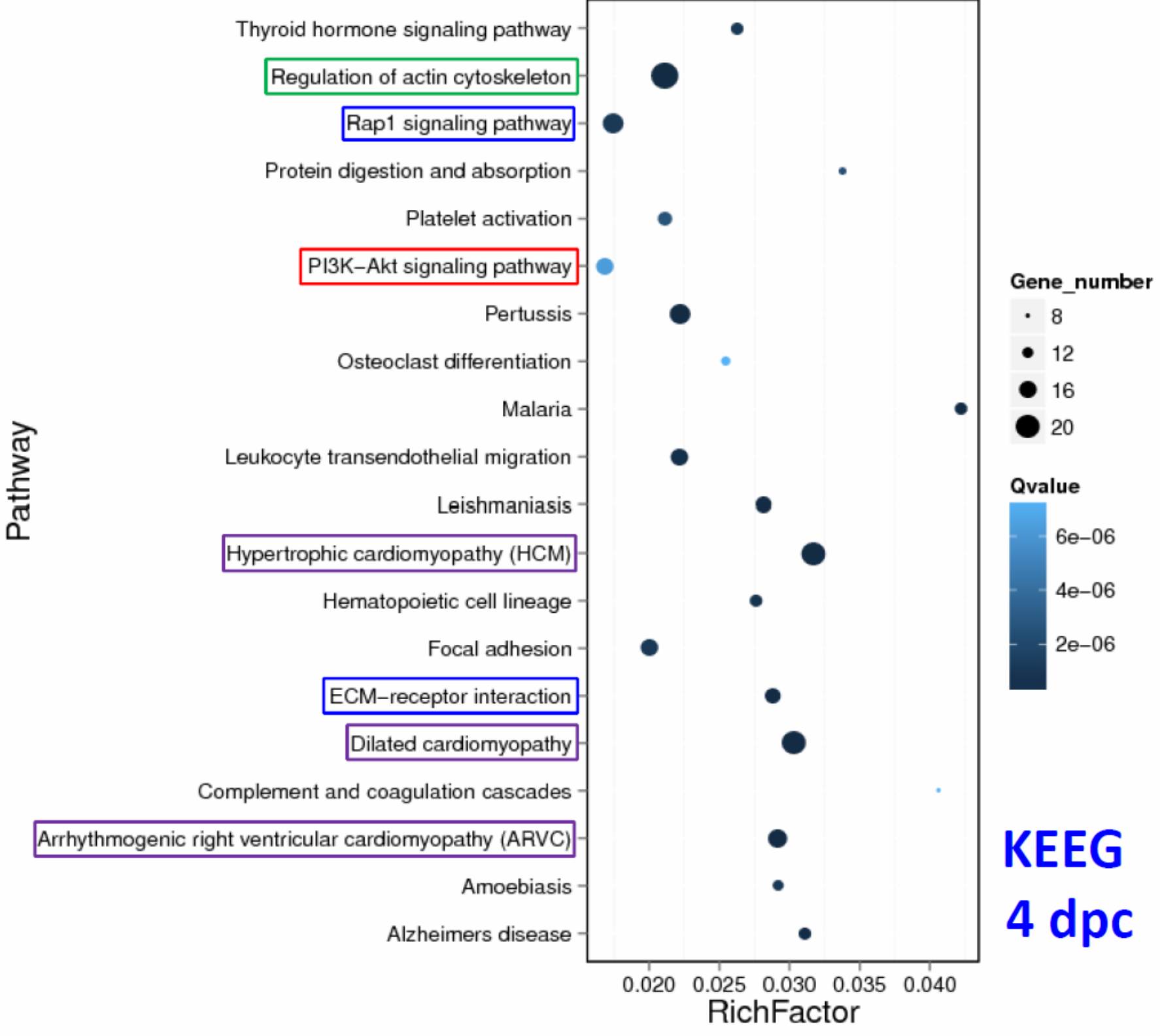
Many critical signaling pathways are activated for cell survival, proliferation, growth, migration and angiogenesis. They regulate the zebrafish heart regeneration after cryoinjury.
Hypothesis
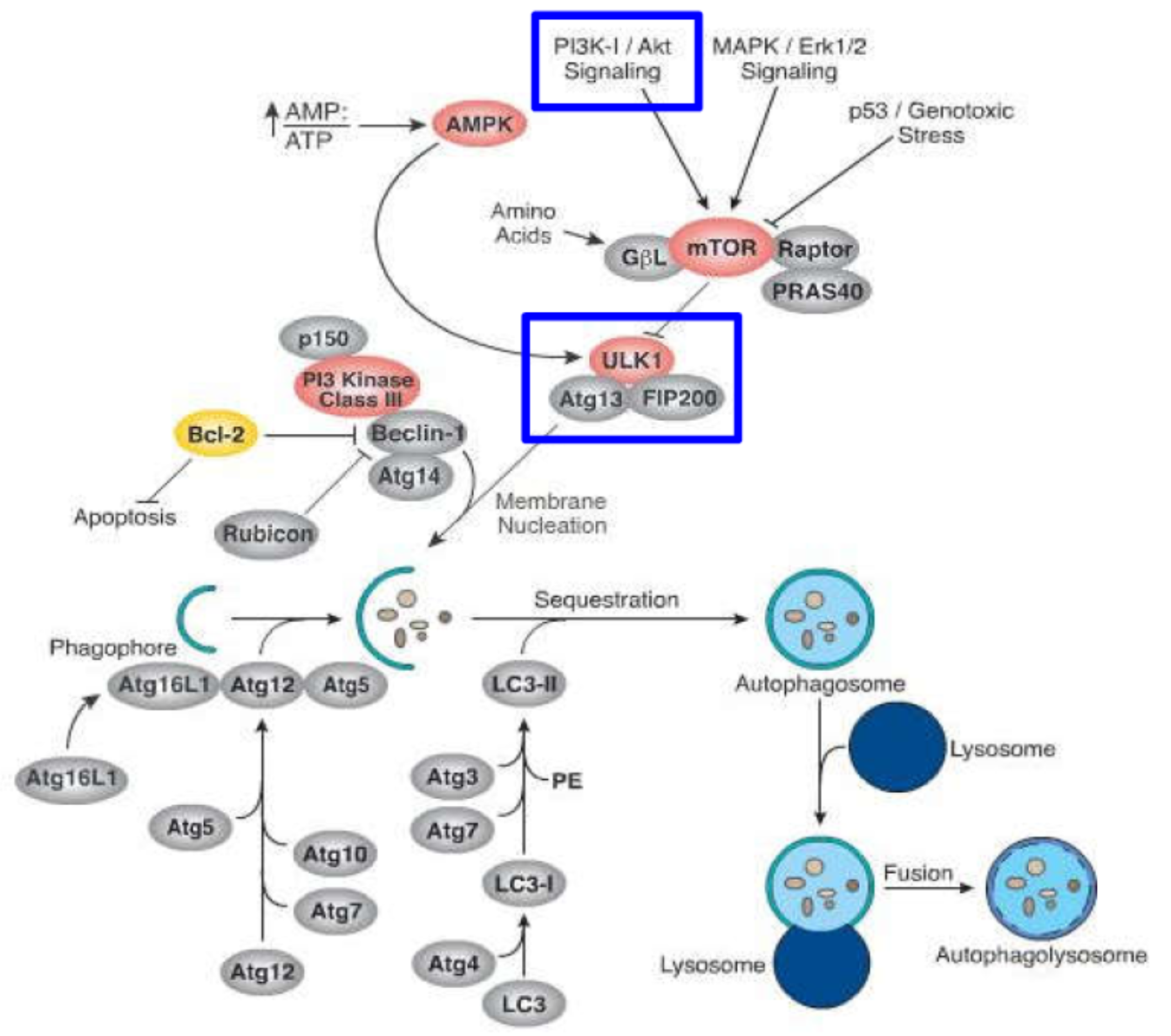
PI3K-AKT signaling pathway mediates the expression of autophagy.
Cellular Senescence: is a program triggered by stresses that prevent abnormal cells from further proliferation.
Senescence-Associated Secretory Phenotype (SASP): in addition to their wellstudied growth arrest, senescent cells display extensive changes in gene expression, including the expression and secretion of many proinflammatory cytokines, chemokines, growth factors, and proteases.
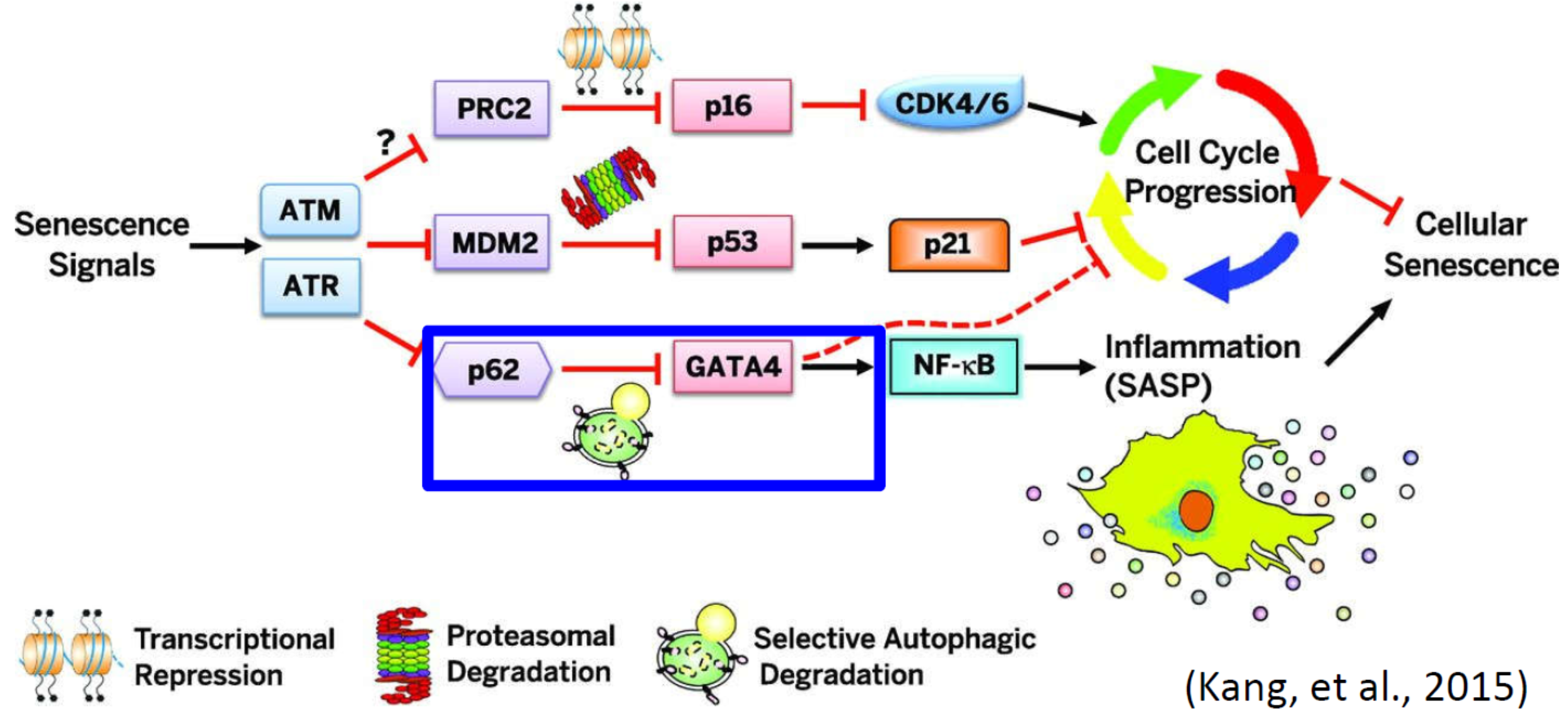
The GATA4 pathway functions independently of the p53 and p16 pathways and is regulated by the DDR kinases ATM and ATR.
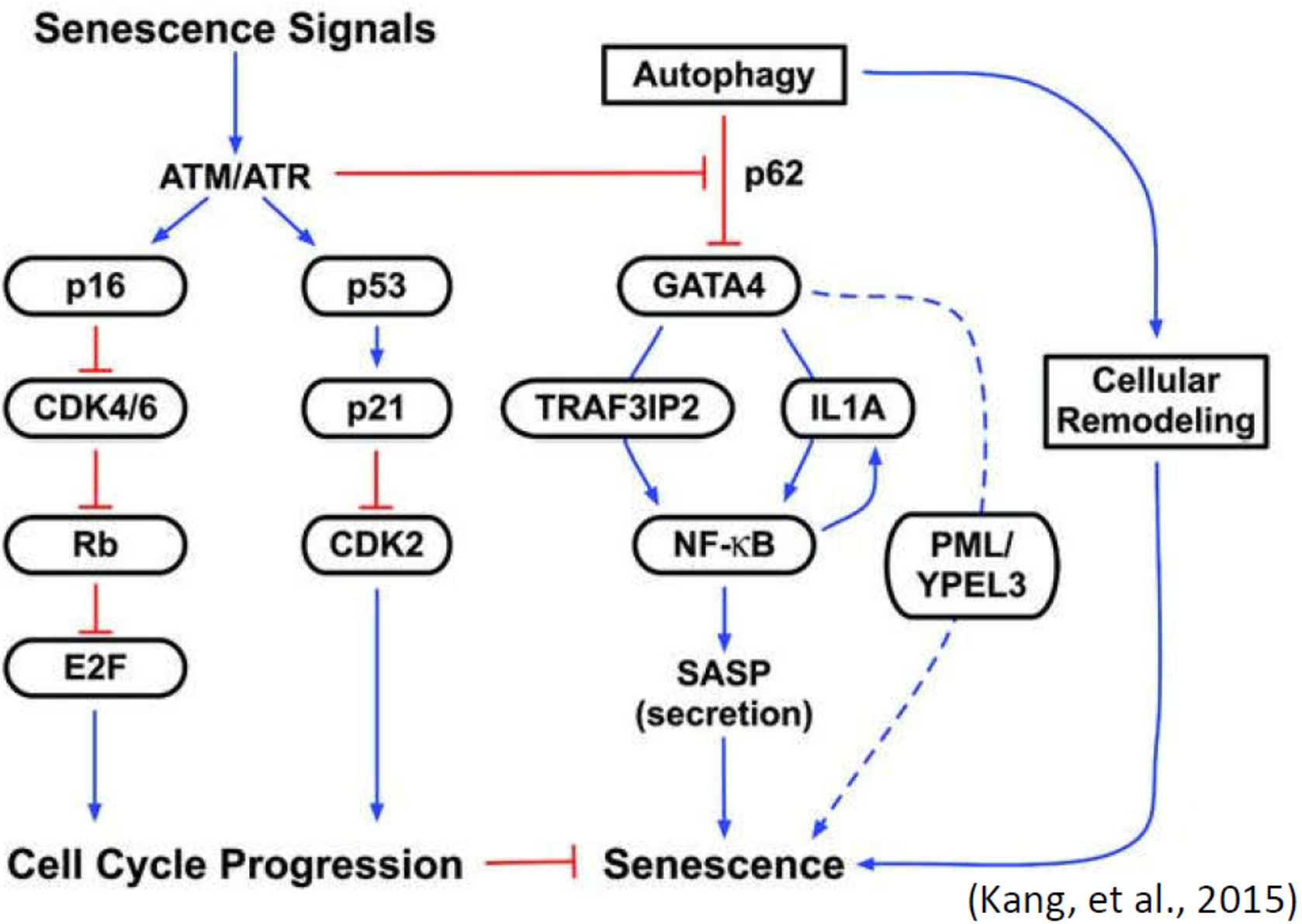
Hypothesis: Autophagy may play an essential role in zebrafish heart regeneration and regulate the expression of GATA4 for myocardial regeneration.
Research Design and Methods
To investigate whether autophagy is required in zebrafish heart regeneration.
To determine whether autophagy regulates the expression of GATA4 for myocardial regeneration.
Use transgenic lines zebrafish embryos to detect their cardiac Research Design and Methods morphogenesis and determine the interaction of autophagy with GATA4 in vivo.