Table of Contents
DNA modification analysis
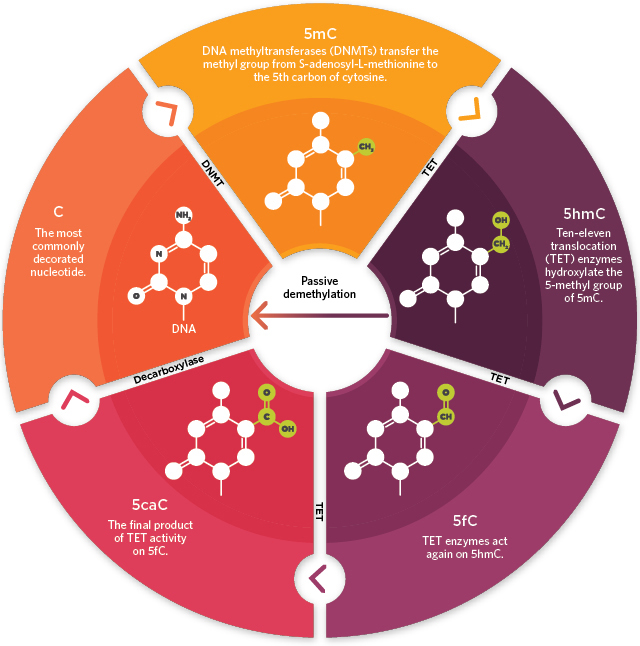
Whole genome DNA methylation detection is one of the most important part of epigenetics research. It is supposed to have a great effect on cancers and tumors, and even be involved in the senility of human. In addition, it is believed that in medical aspects, DNA methylation may have a strong relationship with diabetes and immunological diseases (Jeong et al., 2014; Hackett et al., 2013; Duthie, 2011).
DNA Methylation Prediction
T-BioInfo
Combines statistical analysis modules into pipelines to deal with heterogenous big data. T-BioInfo is an application that can be used for: (1) next-generation sequencing (NGS) data (transcriptomics, genomics/epigenetics, and DNA/RNA); (2) mass-spectroscopy; (3) structural biology; and (4) data integration and modeling (virology, data association, and data mining).
Publications:
Institutions(s):
University of Haifa, Israel Pine Biotech, Haifa, Israel
MethSurv
Correlates overall survival with DNA methylation levels. MethSurv allows to investigate methylation biomarkers that associate with the survival of various human cancers. It combines unsupervised hierarchical clustering and principal component analysis (PCA) for any particular gene. This tool can give a graphical overview of methylation differences between the cancer patients as well as gene subregions.
Publications:
- (Modhukur et al., 2017) MethSurv: a web tool to perform multivariable survival analysis using DNA methylation data Epigenomics.
Institutions(s):
Institute of Computer Science, University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia; United Laboratories of Tartu University Hospital, Tartu University Hospital, Tartu, Estonia.
Nanopolish
Provides a nanopore consensus algorithm using a signal-level hidden Markov model (HMM). The main subprograms of Nanopolish are: (i) nanopolish extract which extracts reads in FASTA or FASTQ format from a directory of FAST5 files; (ii) nanopolish eventalign which aligns signal-level events to k-mers of a reference genome; (iii) nanopolish variants which detects single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and indels with respect to a reference genome; and (iv) nanopolish variants –consensus which calculates an improved consensus sequence for a draft genome assembly. Furthermore, Nanopolish contains an experimental option that will use event durations to improve the consensus accuracy around homopolymers.
Publications:
- (Simpson et al., 2017) Detecting DNA cytosine methylation using nanopore sequencing. Nat Methods.
Institutions(s):
Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, Toronto, Ontario, Canada; Department of Computer Science, University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario, Canada; Department of Biomedical Engineering, Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, USA
DNA Methylation Deconvolution
FaST-LMM-EWASher
An R version of FaST-LMM-EWASher, which performs epigenome-wide association analysis in the presence of confounders such as cell-type heterogeneity. A python version of this software is also available as part of Fast-LMM-Py.
Publications:
- (Zou et al., 2014) Epigenome-wide association studies without the need for cell-type composition. Nat Methods.
Institutions(s):
eScience Research Group, Microsoft Research, Los Angeles, CA, USA; The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA
ReFACTor | Reference-Free Adjustment for Cell-Type composition
A method based on principal component analysis (PCA) and designed for the correction of cell type heterogeneity in epigenome-wide association studies (EWAS). ReFACTor tool is based on a variant of PCA and can be applied to any tissue. It selects the sites that can be reconstructed with low error using a low-rank approximation of the original methylation matrix. Moreover, ReFACTor does not use the phenotype in the selection process, making ReFACTor useful as part of a quality control step in EWAS.
Publications:
- (Rahmani et al., 2016) Sparse PCA corrects for cell type heterogeneity in epigenome-wide association studies. Nat Methods. PMID: 27018579
Institutions(s):
Blavatnik School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel; Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA
EDec | Epigenomic Deconvolution
Provides accurate platform-independent estimation of cell type proportions, DNA methylation profiles and gene expression profiles of constituent cell type. EDec enables deconvolution of complex tumor tissues where highly accurate reference are enables. EDec reveals layers of biological information about distinct cell types within solid tumors and about their heterotypic interactions that were previously inaccessible at such large scale due to tissue heterogeneity.
Publications:
- (Onuchic et al., 2016) Epigenomic Deconvolution of Breast Tumors Reveals Metabolic Coupling between Constituent Cell Types. Cell Rep.
Institutions(s):
Molecular and Human Genetics Department, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX, USA
DNA methylation array analysis
DNA methylation is involved in numerous physiological processes and also disease states, such as cancer (Jones, 2012). This has raised wide interest in developing large-scale DNA methylation profiling technologies to improve our molecular understanding of diseases. The recently released Infinium HumanMethylation450 (Bibikova et al., 2011; Dedeurwaerder et al., 2011) is a preferred technology for studying the DNA methylomes of various cell types in large-scale studies, and there is a current explosion of data generated with this technology (Rakyan et al., 2011). Sequencing-based methods, although offering much higher genome coverage, are still not affordable by all laboratories, notably those with moderate budgets. Another reason for the success of DNA methylation arrays is the ease of reading and understanding the data generated, notably because microarrays have been widely used over the past decades, particularly for gene expression profiling.
Differential Methylation Site Detection
limma | Linear Models for Microarray Data
Provides an integrated solution for analysing data from gene expression experiments. limma contains rich features for handling complex experimental designs and for information borrowing to overcome the problem of small sample sizes. It also contains particularly strong facilities for reading, normalizing and exploring such data. Recently, the capabilities of limma have been significantly expanded in two important directions: (i) it can perform both differential expression and differential splicing analyses of RNA-seq data; (ii) the package is now able to go past the traditional gene-wise expression analyses in a variety of ways, analysing expression profiles in terms of co-regulated sets of genes or in terms of higher-order expression signatures. This provides enhanced possibilities for biological interpretation of gene expression differences.
Publications:
- (Smyth et al., 2005) Use of within-array replicate spots for assessing differential expression in microarray experiments. Bioinformatics.
Institutions(s):
Bioinformatics Division, The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Parkville, VIC, Australia
FastDMA
A software analyzing Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip data, which is featured as multiple core parallel computing.
Publications:
- (Wu et al., 2013) FastDMA: an infinium humanmethylation450 beadchip analyzer. PLoS One.
Institutions(s):
Bioinformatics Division/Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNLIST), Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
RnBeads
An R package for comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation data obtained with any experimental protocol that provides single-CpG resolution, including Infinium 450K microarray and bisulfite sequencing protocols, but also MeDIP-seq and MBD-seq.
Publications:
- (Assenov et al., 2014) Comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation data with RnBeads. Nat Methods.
Institutions(s):
Max Planck Institute for Informatics, Saarbrücken, Germany
Differential Methylation region Detection
ChAMP
Allows Illumina HumanMethylation BeadChip analysis. ChAMP is an integrated analysis pipeline including functions for (i) filtering low quality probes, adjustment for Infinium I and Infinium II probe design, (ii) batch effect correction, detecting differentially methylated positions (DMPs), (iii) finding differentially methylated regions (DMRs) and (iv) detection of copy number aberrations. The software also allows detection of differentially methylated genomic blocks (DMB) and Gene Set Enrichment Analysis (GSEA).
Publications:
- (Morris et al., 2014) ChAMP: 450k Chip Analysis Methylation Pipeline. Bioinformatics.
- (Butcher and Beck, 2015) Probe Lasso: a novel method to rope in differentially methylated regions with 450K DNA methylation data. Methods.
- (Tian et al., 2017) ChAMP: Updated Methylation Analysis Pipeline for Illumina BeadChips. Bioinformatics.
Institutions(s):
CAS Key Lab of Computational Biology, CAS-MPG Partner Institute for Computational Biology, Shanghai Institute for Biological Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai, China
FastDMA
A software analyzing Illumina Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip data, which is featured as multiple core parallel computing.
Publications:
- (Wu et al., 2013) FastDMA: an infinium humanmethylation450 beadchip analyzer. PLoS One.
Institutions(s):
Bioinformatics Division/Center for Synthetic and Systems Biology, Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNLIST), Department of Automation, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
RnBeads
An R package for comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation data obtained with any experimental protocol that provides single-CpG resolution, including Infinium 450K microarray and bisulfite sequencing protocols, but also MeDIP-seq and MBD-seq.
Publications:
- (Assenov et al., 2014) Comprehensive analysis of DNA methylation data with RnBeads. Nat Methods.
Institutions(s):
Max Planck Institute for Informatics, Saarbrücken, Germany
Enrichment Analysis
Over-representation analysis
Blast2GO
Permits functional annotation, management, and data mining of novel sequence data. Blast2GO is based on the utilization of common controlled vocabulary schemas, the gene ontology (GO). It takes in consideration similarity, the extension of the homology, the database of choice, the GO hierarchy, and the quality of the original annotations. This tool is suitable for plant genomics research. It generates functional annotation and assesses the functional meaning of their experimental results.
Publications:
- (Conesa et al., 2005) Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research.
- (Conesa and Götz, 2008) Blast2GO: A comprehensive suite for functional analysis in plant genomics. Int J Plant Genomics.
- (Götz et al., 2008) High-throughput functional annotation and data mining with the Blast2GO suite. Nucleic Acids Res.
Institutions(s):
Bioinformatics Department, Centro de Investigación Príncipe Felipe, Valencia, Spain
g:Profiler
Provides tool to perform functional enrichment analysis and mine additional information. g:Profiler is a web server that allows to characterize and manipulate gene lists of high-throughput genomics. This tool analyses flat or ranked gene lists for enriched features, converts gene identifiers of different classes, maps genes to orthologous genes in related species, finds similarly expressed genes from public microarray and maps human single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) to gene names, chromosomal locations and variant consequence terms from Sequence Ontology (SO).
Publications:
- (Reimand et al., 2011) g:Profiler–a web server for functional interpretation of gene lists (2011 update). Nucleic Acids Res.
- (Reimand et al., 2016) g:Profiler-a web server for functional interpretation of gene lists (2016 update). Nucleic Acids Res.
Institutions(s):
Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, Toronto, ON, Canada; Department of Medical Biophysics, University of Toronto, Toronto, ON, Canada; Institute of Computer Science, University of Tartu, Tartu, Estonia
STEM | Short Time-series Expression Miner
A software program specifically designed for the analysis of short time series microarray gene expression data. STEM implements unique methods to cluster, compare, and visualize such data. STEM also supports efficient and statistically rigorous biological interpretations of short time series data through its integration with the Gene Ontology.
Publications:
- (Ernst and Bar-Joseph, 2006) STEM: a tool for the analysis of short time series gene expression data. BMC Bioinformatics.
Institutions(s):
Center for Automated and Learning and Discovery, School of Computer Science, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh, PA, USA
Gene set enrichment analysis
GSEA | Gene Set Enrichment Analysis
Evaluates microarray data at the level of gene sets. GSEA aims to determine whether members of a gene set S tend to occur toward the top (or bottom) of the list L, in which case the gene set is correlated with the phenotypic class distinction. This method eases the interpretation of a largescale experiment by identifying pathways and processes, and can boost the signal-to-noise ratio when the members of a gene set exhibit strong cross-correlation, allowing to detect modest changes in individual genes.
Publications:
- (Subramanian et al., 2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.
- (Mootha et al., 2003) PGC-1alpha-responsive genes involved in oxidative phosphorylation are coordinately downregulated in human diabetes. Nat Genet.
Institutions(s):
Broad Institute of Massachusetts Institute of Technology and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA; Department of Systems Biology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
DESeq | Differential expression : HTS analysis
Performs differential gene expression analysis. DEseq is a method that integrates methodological advances with features to facilitate quantitative analysis of comparative RNA-seq data using shrinkage estimators for dispersion and fold change. The software is suitable for small studies with few replicates as well as for large observational studies. Its heuristics for outlier detection assist in recognizing genes for which the modeling assumptions are unsuitable and so avoids type-I errors caused by these.
Publications:
- (Love et al., 2014) Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol.
- (Anders and Huber, 2010) Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol.
Institutions(s):
Department of Biostatistics and Computational Biology, Dana Farber Cancer Institute, Boston, MA, USA; Department of Biostatistics, Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, MA, USA
edgeR | empirical analysis of DGE in R
Allows differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. edgeR implements a range of statistical methodology based on the negative binomial distributions, including empirical Bayes estimation, exact tests, generalized linear models and quasi likelihood tests. The package and methods are general, and can work on other sources of count data, such as barcoding experiments and peptide counts.
Publications:
- (Robinson et al., 2010) edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics.
Institutions(s):
Cancer Program, Garvan Institute of Medical Research, Darlinghurst, NSW, Australia; Bioinformatics Division, The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Parkville, VIC, Australia
Topology enrichment analysis
DAVID | Database for Annotation, Visualization and Integrated Discovery
Allows users to obtain biological features/meaning associated with large gene or protein lists. DAVID can determine gene-gene similarity, based on the assumption that genes sharing global functional annotation profiles are functionally related to each other. It groups related genes or terms into functional groups employing the similarity distances measure. This tool takes into account the redundant and network nature of biological annotation contents.
Publications:
- (Jiao et al., 2012) DAVID-WS: a stateful web service to facilitate gene/protein list analysis. Bioinformatics.
- (Huang da et al., 2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc. * (Huang da et al., 2009) Bioinformatics enrichment tools: paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res.
Institutions(s):
Laboratory of Immunopathogenesis and Bioinformatics, Frederick, MD, USA; Advanced Biomedical Computing Center, Frederick, MD, USA
HOMER | Hypergeometric Optimization of Motif EnRichment
Performs peak finding and downstream data analysis for next-generation sequencing analysis. HOMER affords several tools and methods to make use of ChIP-Seq, GRO-Seq, RNA-Seq, DNase-Seq, Hi-C and other types of functional genomics sequencing data sets. This software offers support to UCSC visualization, peaks annotation, quantification of transcripts and repeats or differential features, enrichment and expression.
Publications:
- (Heinz et al., 2010) Simple combinations of lineage-determining transcription factors prime cis-regulatory elements required for macrophage and B cell identities. Mol Cell.
Institutions(s):
Department of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA; Department of Medicine, University of California, San Diego, La Jolla, CA, USA
GeneCodis | Topology enrichment analysis
A web-based tool for the ontological analysis of large lists of genes. It can be used to determine biological annotations or combinations of annotations that are significantly associated to a list of genes under study with respect to a reference list. As well as single annotations, this tool allows users to simultaneously evaluate annotations from different sources, for example Biological Process and Cellular Component categories of Gene Ontology.
Publications:
- (Tabas-Madrid et al., 2012) GeneCodis3: a non-redundant and modular enrichment analysis tool for functional genomics. Nucleic Acids Res.
Institutions(s):
Functional Bioinformatics Group, National Center for Biotechnology (CNB-CSIC), Madrid, Spain
Bisulfite Sequencing Data Analysis (BS-seq analysis)
DNA methylation contributes to the epigenetic regulation of many key developmental processes including genomic imprinting, X-inactivation, genome stability and gene regulation. Bisulfite conversion of genomic DNA combined with next-generation sequencing (BS-seq) is widely used to measure the methylation state of a whole genome, the methylome, at single-base resolution (Lister et al., 2009; Bock et al., 2010; Harris et al., 2010).
Differential Methylation region Detection
methylKit | Methylation annotation : BS-seq analysis
An R package for DNA methylation analysis and annotation from high-throughput bisulfite sequencing. methylKit is designed to deal with sequencing data from RRBS and its variants, but also target-capture methods such as Agilent SureSelect methyl-seq. In addition, methylKit can deal with base-pair resolution data for 5hmC obtained from Tab-seq or oxBS-seq. It can also handle whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data if proper input format is provided.
Publications:
- (Akalin et al., 2012) methylKit: a comprehensive R package for the analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation profiles. Genome Biol.
Institutions(s):
Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, USA
SMART | Specific Methylation Analysis and Report Tool
Detects the cell type-specific methylation marks by integrating multiple methylomes from human cell lines and tissues. SMART is an entropy-based framework focused on integrating of a large number of DNA methylomes for the de novo identification of cell type-specific MethyMarks. To facilitate the specific methylation analysis, this method dynamically integrates multiple methylomes and identifies the cell type-specific methylation marks.
Publications:
- (Liu et al., 2016) Systematic identification and annotation of human methylation marks based on bisulfite sequencing methylomes reveals distinct roles of cell type-specific hypomethylation in the regulation of cell identity genes. Nucleic Acids Res.
Institutions(s):
College of Bioinformatics Science and Technology, Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China; Department of Rehabilitation, the First Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin, China
DSS-single | Differentially methylated region detection : BS-seq analysis
A package based on a statistical method for detecting DMRs from WGBS (Whole Genome Bisulfite Sequencing) data without replicates. A key feature of DSS-single is to estimate biological variation when replicated data are not available. The method takes advantage of the spatial correlation of methylation levels: since the methylation levels from nearby CpG sites are similar, we can use nearby CpG sites as ‘pseudo-replicates’ to estimate dispersion. Simulations demonstrate that DSS-single has greater sensitivity and accuracy than existing methods, and an analysis of H1 versus IMR90 cell lines suggests that it also yields the most biologically meaningful results.
Publications:
- (Feng et al., 2014) A Bayesian hierarchical model to detect differentially methylated loci from single nucleotide resolution sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res.
Institutions(s):
Department of Biostatistics and Bioinformatics, Rollins School of Public Health, Emory University, Atlanta, GA, USA
Methylation Annotation
GBSA | Genome Bisulfite Sequencing Analyser
An open-source software tool capable of analysing whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data with either a gene-centric or gene-independent focus. GBSA’s output can be easily integrated with other high-throughput sequencing data, such as RNA-Seq or ChIP-seq, to elucidate the role of methylated intergenic regions in gene regulation. In essence, GBSA allows an investigator to explore not only known loci but also all the genomic regions, for which methylation studies could lead to the discovery of new regulatory mechanisms.
Publications:
- (Benoukraf et al., 2013) GBSA: a comprehensive software for analysing whole genome bisulfite sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res.
Institutions(s):
Cancer Science Institute of Singapore, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore; Department of Pathology, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore
methylKit | Methylation annotation : BS-seq analysis
An R package for DNA methylation analysis and annotation from high-throughput bisulfite sequencing. methylKit is designed to deal with sequencing data from RRBS and its variants, but also target-capture methods such as Agilent SureSelect methyl-seq. In addition, methylKit can deal with base-pair resolution data for 5hmC obtained from Tab-seq or oxBS-seq. It can also handle whole-genome bisulfite sequencing data if proper input format is provided.
Publications:
- (Akalin et al., 2012) methylKit: a comprehensive R package for the analysis of genome-wide DNA methylation profiles. Genome Biol.
Institutions(s):
Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, USA
EWAS
ReFACTor | Reference-Free Adjustment for Cell-Type composition
A method based on principal component analysis (PCA) and designed for the correction of cell type heterogeneity in epigenome-wide association studies (EWAS). ReFACTor tool is based on a variant of PCA and can be applied to any tissue. It selects the sites that can be reconstructed with low error using a low-rank approximation of the original methylation matrix. Moreover, ReFACTor does not use the phenotype in the selection process, making ReFACTor useful as part of a quality control step in EWAS.
Publications:
- (Rahmani et al., 2016) Sparse PCA corrects for cell type heterogeneity in epigenome-wide association studies. Nat Methods. PMID: 27018579
Institutions(s):
Blavatnik School of Computer Science, Tel-Aviv University, Tel Aviv, Israel; Department of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, CA, USA
FaST-LMM-EWASher
An R version of FaST-LMM-EWASher, which performs epigenome-wide association analysis in the presence of confounders such as cell-type heterogeneity. A python version of this software is also available as part of Fast-LMM-Py.
Publications:
- (Zou et al., 2014) Epigenome-wide association studies without the need for cell-type composition. Nat Methods.
Institutions(s):
eScience Research Group, Microsoft Research, Los Angeles, CA, USA; The Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA