Phenomics is an area of biology concerned with the measurement of phenomes (a phenome is the set of physical and biochemical traits belonging to a given organism) as they change in response to genetic mutation and environmental influences. It is used in functional genomics, pharmaceutical research, metabolic engineering and increasingly in phylogenetics.
A key goal of biology is to understand phenotypic characteristics, such as health, disease and evolutionary fitness. Phenotypic variation is produced through a complex web of interactions between genotype and environment, and such a ‘genotype–phenotype’ map is inaccessible without the detailed phenotypic data that allow these interactions to be studied. Source
Including:
- Microscopic Phenotype Analysis
- Laser Scanning Microscopy
- Conventional Fluorescence microscopy
- Super-resolution Imaging
- Cryo-EM
Including:
- Medical Imaging Analysis
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Computerized Tomography Scan Imaging
- Nuclear Medicine Imaging
- Ultrasonic Imaging
Including:
- Realistic Neuronal Network Modelling
- Compartment Neuron Modelling
- Model Files Conversion
- Model Files Visualization
- Model Building
- Database
Including:
- Neurophysiology Analysis
- Clinical Eletrophysiology
- Patch-clamp
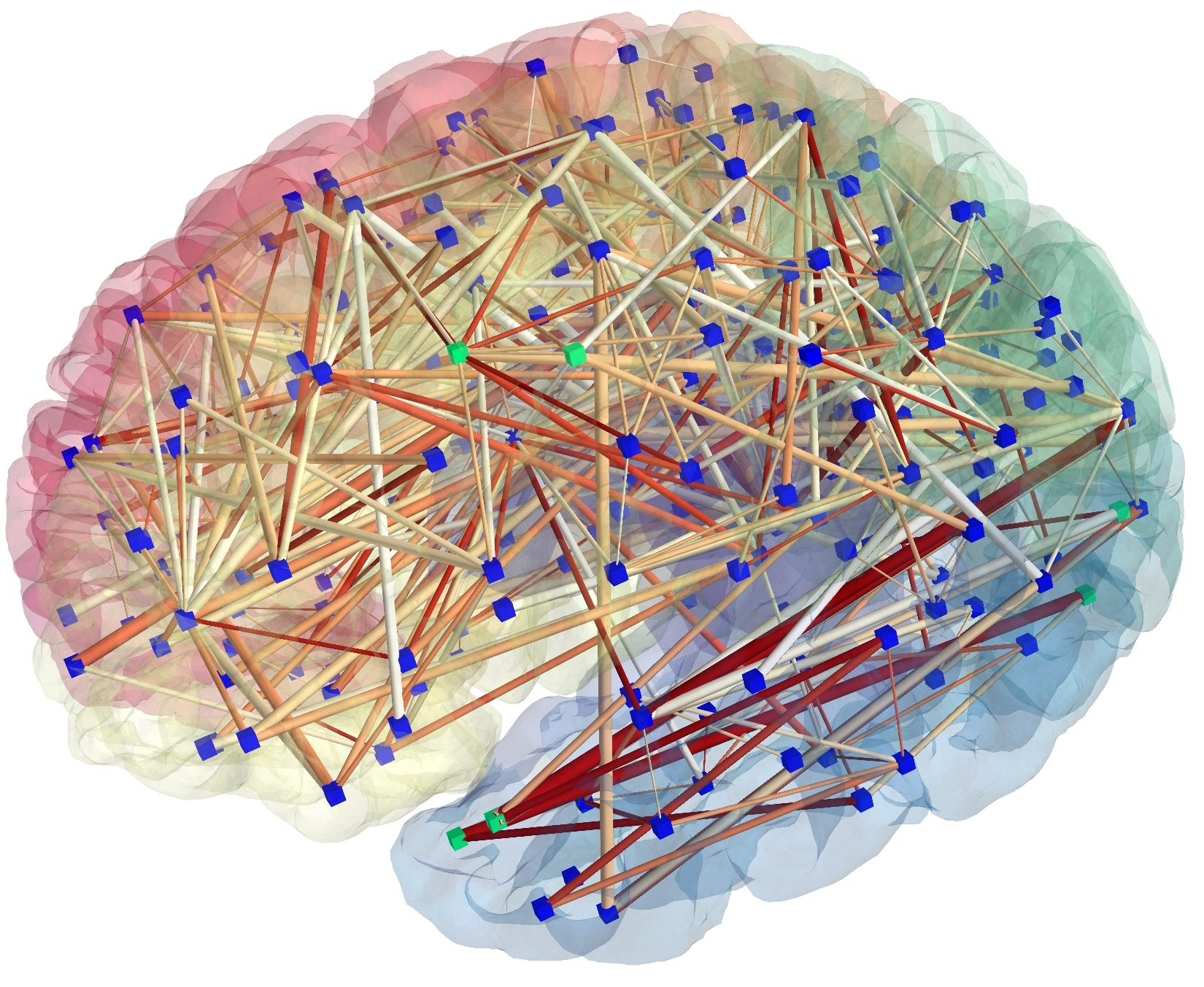
Including:
- Connectivity Analysis
- Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging
- Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging Analysis
- Neuron Tracing